Tube thoracostomy
- Home
- Services
- Pulmonology
- Tube thoracostomy
Tube thoracostomy, often referred to as chest tube insertion, is a crucial medical procedure used to treat various conditions affecting the chest cavity, particularly those involving fluid or air accumulation that compromises lung function. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of tube thoracostomy, its indications, procedure details, and recovery aspects.
What is Tube Thoracostomy?
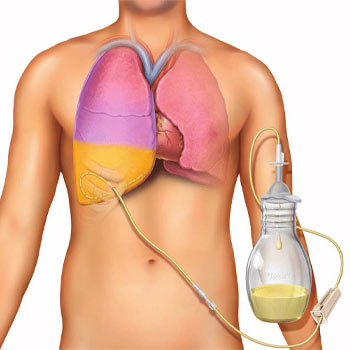
Tube thoracostomy is a medical procedure involving the insertion of a chest tube into the pleural space, the area between the lungs and the chest wall. This space is crucial for maintaining lung expansion and functionality. The procedure is performed to drain accumulated air, blood, or fluid from the pleural cavity, thereby alleviating pressure on the lungs and allowing them to re-expand fully.
When should Tube Thoracostomy be considered?
Tube thoracostomy is indicated in several medical conditions where the accumulation of air or fluid in the pleural space compromises lung function or poses significant health risks. Common indications include
Pneumothorax
This condition occurs when air accumulates in the pleural space, causing lung collapse and potentially leading to respiratory distress
Hemothorax
Involves the accumulation of blood in the pleural cavity, often due to trauma, surgery, or underlying medical conditions
Pleural Effusion
Refers to the buildup of fluid in the pleural space, which can result from infections, heart failure, cancer, or liver disease, among other causes
Empyema
A condition characterized by the presence of infected fluid (pus) in the pleural cavity, typically due to bacterial infections.
What are the key steps involved in performing a tube thoracostomy?
The tube thoracostomy procedure involves several key steps
Patient Preparation
The patient is positioned appropriately, usually lying on the affected side or in a semi-upright position. Local anesthesia is administered to numb the insertion site, which is typically in the mid-axillary line (the side of the chest)
Insertion of Chest Tube
A small incision is made in the skin, and a hollow tube (chest tube) is carefully inserted through the chest wall into the pleural space. The tube is then connected to a drainage system that allows for the controlled removal of air, fluid, or blood from the chest cavity
Monitoring and Management
Once the tube is in place, its position is confirmed via chest X-ray or ultrasound. Healthcare providers monitor the drainage and the patient's respiratory status closely to ensure effective lung re-expansion and optimal drainage
Post-procedure Care
After tube insertion, patients may require pain management and ongoing monitoring to assess drainage volume, respiratory function, and potential complications
What are the advantages of undergoing Tube Thoracostomy?
Tube thoracostomy offers significant benefits in managing conditions such as pneumothorax and pleural effusion by
Facilitating Lung Re-expansion
By draining excess air or fluid, the procedure helps the lungs re-expand fully, restoring respiratory function.
However, like any medical procedure, tube thoracostomy carries certain risks, including infection, bleeding, tube malposition, and damage to surrounding structures. These risks are mitigated through careful patient selection, skilled procedural technique, and vigilant post-procedure care
How should follow-up care be managed after a tube thoracostomy procedure?
Following tube thoracostomy, recovery varies depending on the underlying condition and the patient's overall health. Most patients experience relief from symptoms related to lung collapse or fluid buildup shortly after the procedure. Close monitoring continues to ensure proper drainage and assess for any signs of complications.
Tube thoracostomy is a critical intervention in pulmonology, addressing conditions that compromise lung function and pose significant health risks. By understanding its indications, procedure details, and recovery aspects, healthcare providers and patients alike can appreciate its lifesaving potential. Effective communication and patient education are essential in ensuring optimal outcomes and improving quality of life for individuals undergoing this procedure
For more information or to discuss your specific medical concerns regarding tube thoracostomy, consult with your healthcare provider. Understanding the procedure's benefits and risks empowers patients and caregivers to make informed decisions regarding their respiratory health
