FNAC of lymph nodes & lung lesions
- Home
- Services
- Pulmonology
- FNAC of lymph nodes & lung lesions
What is FNAC of Lymph Nodes & Lung Lesions?
Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) is a diagnostic procedure used in pulmonology to investigate abnormalities in lymph nodes and lung lesions. This minimally invasive technique involves extracting tissue or fluid samples using a thin needle for microscopic examination. FNAC plays a crucial role in diagnosing various pulmonary conditions, offering valuable insights without the need for more invasive procedures
What does the procedure of FNAC of Lymph Nodes involve?
FNAC begins with the patient positioned comfortably, typically either sitting or lying down, depending on the location of the lymph node or lesion. The skin overlying the area of interest is cleansed, and local anesthesia may be administered to minimize discomfort. Using imaging guidance such as ultrasound or CT scan for precision, a fine needle is inserted into the lymph node or lesion. The needle is then manipulated to obtain a sample, which may consist of cells or fluid depending on the nature of the lesion
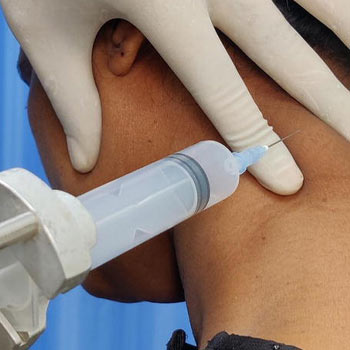
What does the procedure for FNAC of Lymph Nodes involve?
FNAC serves multiple diagnostic purposes in pulmonology
Diagnosis of Lung Lesions
FNAC is instrumental in evaluating suspicious lung nodules or masses detected on imaging studies like chest X-rays or CT scans. By analyzing cellular morphology and architecture, FNAC helps differentiate between benign and malignant lesions
Assessment of Lymph Nodes
Enlarged lymph nodes in the chest cavity (mediastinum) or elsewhere in the body can indicate various conditions, including infections, inflammation, or cancer. FNAC aids in determining the underlying cause by examining cellular characteristics of the lymph node tissue
Advantages of FNAC
- Minimally Invasive: FNAC is less invasive compared to surgical biopsy, reducing the risk of complications and promoting faster recovery
- Quick Results: Results from FNAC are often available promptly, allowing for timely diagnosis and treatment planning
- Accuracy: When performed by skilled professionals and complemented by adequate imaging guidance, FNAC yields high diagnostic accuracy in distinguishing between benign and malignant conditions
Indications for FNAC
FNAC may be indicated in the following scenarios
- Evaluation of Lung Nodules: To determine if a lung nodule is cancerous or benign
- Assessment of Mediastinal Lymph Nodes: To investigate enlarged lymph nodes detected on imaging
- Monitoring Treatment Response: FNAC can be used to assess changes in tumor characteristics during treatment
Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) is a valuable tool in pulmonology for diagnosing lymph node and lung lesions. By providing rapid and accurate diagnostic information, FNAC aids clinicians in making informed decisions regarding patient management and treatment strategies. This minimally invasive procedure continues to play a pivotal role in the comprehensive care of patients with pulmonary conditions, ensuring timely diagnosis and optimized outcomes
