pleural biopsy
- Home
- Services
- Pulmonology
- pleural biopsy
What is Pleural Biopsy?
Pleural biopsy is a diagnostic procedure used to obtain tissue samples from the pleura, the thin membrane surrounding the lungs. This procedure is crucial in diagnosing various pulmonary and pleural conditions, allowing healthcare providers to determine the cause of symptoms such as chest pain, coughing, or difficulty breathing. Here's a comprehensive guide to understanding pleural biopsy, its types, procedure, indications, risks, and recovery:
Why is Pleural Biopsy Performed?
Pleural biopsy is primarily performed to investigate and diagnose conditions that affect the pleura. These conditions may include
- Pleural Effusion: A buildup of fluid in the pleural space, which can be caused by infections, heart failure, cancer, or other medical conditions
- Pleural Thickening: Abnormal thickening of the pleura, often associated with asbestos exposure or certain infections
- Pleural Tumors: Both benign and malignant tumors that originate from the pleura or spread to the pleural space from other parts of the body
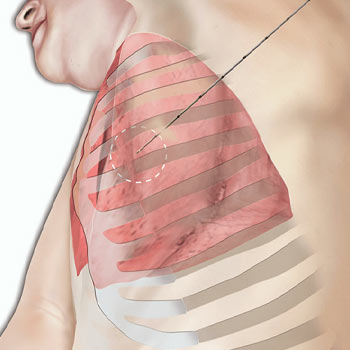
What are the types of Pleural Biopsy?
There are several methods used to perform a pleural biopsy
Closed Pleural Biopsy
Also known as needle biopsy or Abram's needle biopsy, this method involves inserting a thin needle through the chest wall into the pleural space to collect tissue samples. It is often guided by imaging techniques like ultrasound or CT scan to ensure accuracy
Thoracoscopic Biopsy
This is a minimally invasive procedure where a thoracoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera) is inserted through a small incision in the chest wall. This allows the surgeon to directly visualize the pleura and obtain biopsy samples with greater precision.
Open Surgical Biopsy
In cases where other methods are inconclusive or unavailable, an open surgical biopsy may be performed. This involves making a larger incision in the chest wall under general anesthesia to access the pleura and obtain tissue samples.
What is the procedure of Pleural Biopsy?
The specific procedure for pleural biopsy depends on the type chosen by the healthcare provider. Generally, it involves the following steps
Preparation
The patient may undergo imaging tests such as chest X-rays or CT scans to locate the precise area for biopsy. Blood tests may also be conducted to assess overall health and clotting factors
Anesthesia
Depending on the type of biopsy, local anesthesia (for closed biopsy) or general anesthesia (for thoracoscopic or open surgical biopsy) may be administered to ensure comfort during the procedure.
Biopsy
The biopsy procedure itself involves inserting the biopsy needle or thoracoscope through the chest wall into the pleural space. Tissue samples are collected and sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Closure
After obtaining the samples, any incisions made are closed with sutures or adhesive bandages.
What are the indications for Pleural Biopsy?
Pleural biopsy is indicated in various clinical scenarios, including
- Diagnosis of Pleural Effusions: To determine the underlying cause of fluid accumulation in the pleural space
- Evaluation of Pleural Thickening: To investigate abnormal thickening of the pleura, which may indicate conditions like mesothelioma or tuberculosis
- Identification of Cancer: To confirm or rule out cancerous growths affecting the pleura
- Assessment of Infections: To diagnose infectious diseases such as tuberculosis or fungal infections affecting the pleura
How long does it take to recover from a Pleural Biopsy procedure?
Recovery from pleural biopsy depends on the type of procedure performed and individual health factors. Generally, patients are monitored for a few hours post-procedure for any immediate complications. They may be advised to avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting for a few days. Results from the biopsy are typically available within a few days to a week, allowing healthcare providers to proceed with appropriate treatment based on the findings
Pleural biopsy is a valuable diagnostic tool in pulmonology, allowing for the accurate diagnosis of various pulmonary and pleural conditions. Understanding the procedure, its indications, risks, and recovery process is essential for patients and healthcare providers alike in making informed decisions regarding treatment and management strategies. If you have concerns about pleural biopsy or its implications for your health, consult with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and care.
